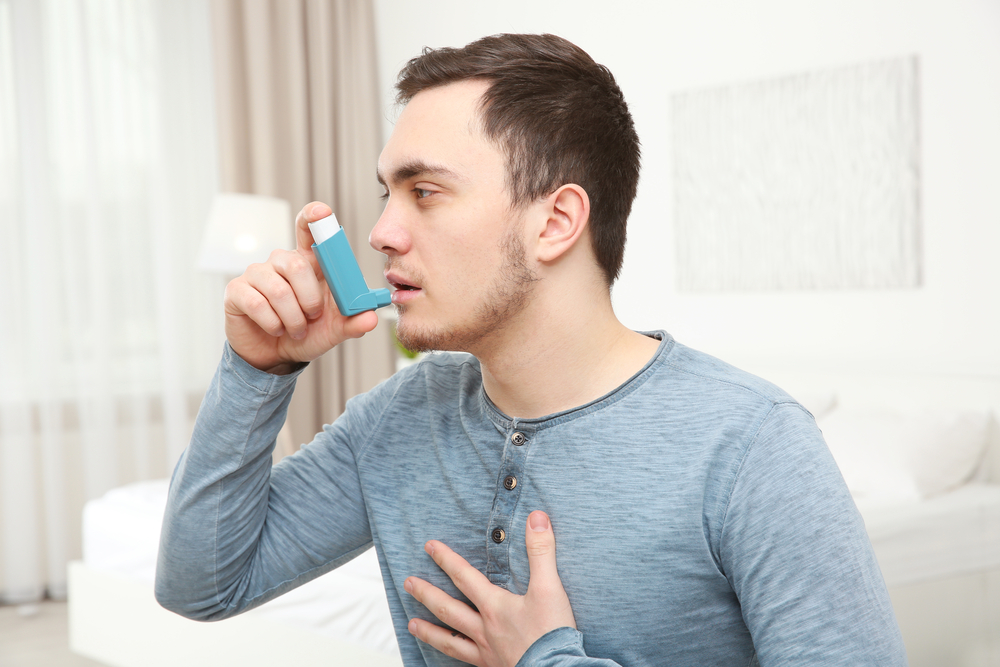
If you have difficulties breathing when exercising, you may have been diagnosed with asthma. There is a lesser known cause of breathing difficulties when exercising and it is called Exercise Inducted Laryngeal Obstruction (EILO). It used to be called Paradoxical Vocal Fold Motion. The symptoms are only present with more intense exercise, near your maximum effort, and you will find it difficult to get air into your lungs. It often causes you to feel distressed and stop you exercising to get your breath back. The difference to asthma is that you can’t get air into your lungs rather than difficulty getting air back out of your lungs. The difficulty with breathing is caused by the vocal cords or false vocal cords moving together when you are breathing in, creating more resistance and requiring more effort from your respiratory muscles. Normally the vocal cords would be wide open when you are breathing in.
If you have asthma instead of EILO, your asthma medications would work to allow normal breathing when exercising. The other main difference, as mentioned before, is that you will find it difficult to breathe out rather than in if you have asthma rather than EILO.
So, what can be done if you think you have EILO? One of the first things to try is slowing your inspiration by slightly pursing your lips or breathing through your teeth. Breathing using more of your diaphragm rather than accessory muscles of respiration when you get symptoms on intense exercise can also help. People with EILO are thought to have increased ventilation rates compared to asymptomatic individuals and this increased air flow may irritate the larynx, causing contraction of the vocal cords and false vocal cords when they should be relaxed. They also have an altered breathing pattern, with less diaphragm use and reduced lower rib expansion on inspiration.
If you suffer from gastric reflux, dealing with this may also help to make your larynx less sensitized and lessen the vocal cord narrowing on inspiration.
More invasive techniques involve removing part of the tissue in your larynx to reduce narrowing at the vocal cords and false vocal cords. This also removes some of the muscle that can be contracting to cause narrowing of the larynx on inspiration.
If you think you have EILO, an assessment of your breathing when exercising and instruction in breathing techniques may help you.